Herpetic Folliculitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Demystified
Are you experiencing an itchy, painful rash that seems to be spreading? It could be herpetic folliculitis, a common but often misunderstood condition. Whether you’ve just been diagnosed or are simply curious about this condition, this article will provide you with all the essential information you need.
Herpetic folliculitis is a viral infection that affects the hair follicles, causing inflammation and discomfort. It is primarily caused by the herpes simplex virus, which can be easily transmitted through direct contact with an infected individual or by sharing personal items such as towels or razors.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for herpetic folliculitis. From understanding the underlying triggers to exploring various management techniques, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge to identify and address this condition effectively.
Table Of Contents
- Herpetic Folliculitis: What is it?
- Herpetic Folliculitis: Causes
- Herpetic Folliculitis: Symptoms
- Herpetic Folliculitis: Diagnosis
- Herpetic Folliculitis: Treatment Options
- Herpetic Folliculitis: Prevention Tips
- Herpetic Folliculitis: Complications
- The Takeaway
Herpetic Folliculitis: What is it?
Herpetic folliculitis is a viral infection that affects the hair follicles and surrounding skin. It is triggered by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is the same virus responsible for cold sores and genital herpes. When the virus enters the body, it can lie dormant in nerve cells for long periods before becoming active. Once activated, it travels to the skin surface and causes the characteristic symptoms of herpetic folliculitis.
The virus is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or by coming into contact with items that have been contaminated with the virus, such as towels or razors. It is important to note that herpetic folliculitis is different from regular folliculitis, which is caused by bacterial or fungal infections. Understanding the distinction is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Herpetic folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where hair follicles are present, but it is most commonly found on the face, neck, chest, and back. The condition can affect people of all ages and genders, although it is more common in individuals who are immunocompromised or those who have a history of other herpes infections.
Herpetic Folliculitis: Causes
As mentioned earlier, herpetic folliculitis is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two types of HSV: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 is commonly associated with oral herpes, while HSV-2 is primarily associated with genital herpes. However, both types of the virus can cause herpetic folliculitis.
The virus is highly contagious and can be readily transmitted through direct contact with an infected individual or by touching items that have been in contact with the virus, such as towels or razors. Additionally, it can be transmitted through sexual contact or by sharing personal items, such as utensils or lip balms.
Once the virus enters the body, it can lie dormant in nerve cells for extended periods. Certain factors can trigger the activation of the virus, leading to the development of herpetic folliculitis. These triggers can include stress, illness, hormonal changes, excessive sun exposure, and a weakened immune system.
It is worth noting that herpetic folliculitis is not a result of poor hygiene or personal care. The virus is highly contagious and can affect anyone, regardless of their cleanliness or lifestyle choices.
Herpetic Folliculitis: Symptoms
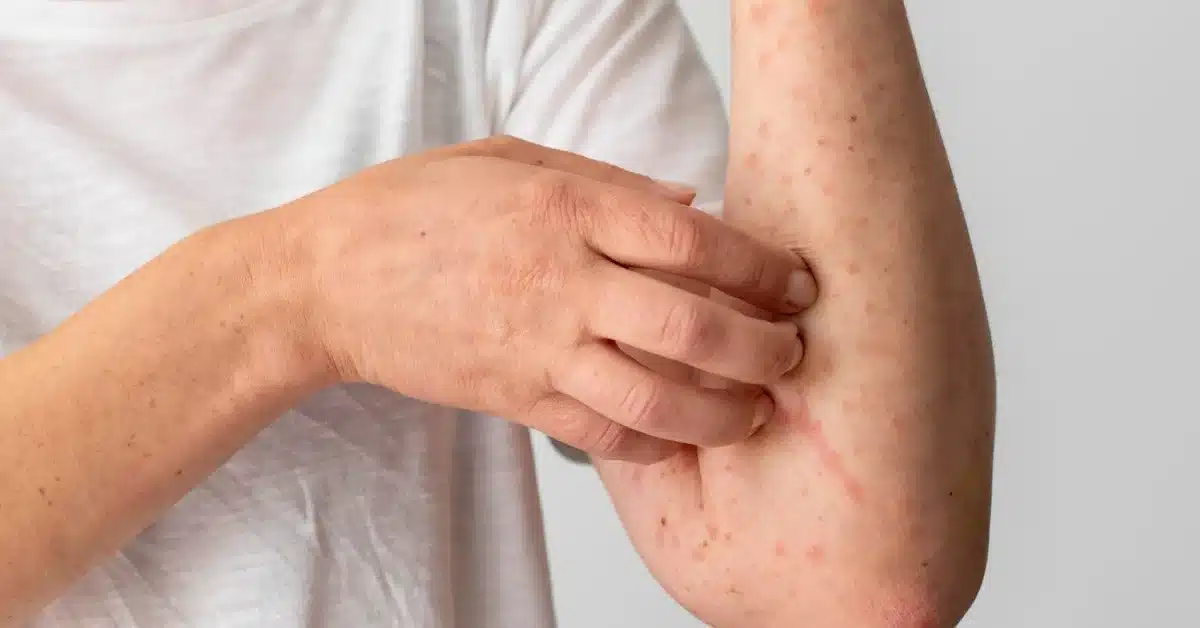
Herpetic folliculitis presents with several distinct symptoms that can vary in severity from person to person. The first sign is often a tingling or burning sensation in the affected area, followed by the appearance of small, red bumps or blisters. These bumps may be filled with clear or yellowish fluid and can be itchy and painful.
Over time, the bumps may burst, releasing the fluid and forming crusts. The crusts will eventually heal, leaving behind scabs that will fall off as the skin heals. The entire cycle can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the individual’s immune response and the severity of the infection.
In some cases, herpetic folliculitis can be accompanied by flu-like symptoms, such as headache, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms are more common in individuals with weakened immune systems or those experiencing a severe outbreak.
It is important to note that herpetic folliculitis can often be misinterpreted as other skin conditions, such as acne, regular folliculitis or vaginal folliculitis, caused by bacteria or fungi. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis. Speaking of diagnosis, let’s explore how herpetic folliculitis is diagnosed.
Herpetic Folliculitis: Diagnosis
Diagnosing herpetic folliculitis usually involves a combination of physical examination and laboratory tests. During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will examine the affected area and take note of the characteristic symptoms, such as red bumps or blisters. The healthcare professional will also look for other bacterial skin infections, such as cellulitis or impetigo, to ensure comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment.
In some cases, the healthcare professional may perform a viral culture by taking a sample of fluid from the blisters or using a cotton swab to gather a sample from the affected area. The sample is sent to a laboratory for further analysis to determine the presence of the herpes simplex virus.
In addition to viral cultures, other laboratory tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests or blood tests, may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis. These tests can detect the presence of HSV antibodies in the blood or identify the genetic material of the virus.
It is important to undergo proper medical diagnosis to ensure accurate treatment and prevent the spread of the virus.
Herpetic Folliculitis: Treatment Options
Treatment for herpetic folliculitis aims to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent future outbreaks. There are several treatment options available, including antiviral medications, topical creams, and home remedies; here are the common ones:
1. Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir, are commonly prescribed to treat herpetic folliculitis. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus, reducing the severity of symptoms, and speeding up the healing process. They are most effective when taken at the first sign of an outbreak.
2. Topical Creams and Ointments
Topical creams containing antiviral agents, such as docosanol or penciclovir, can also be used to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These creams are applied directly to the affected area and can help reduce pain, itching, and the duration of outbreaks.
3. Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may be recommended to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with herpetic folliculitis.
4. Warm Compresses
Applying warm compresses to the affected areas can help soothe the skin, reduce inflammation, and promote the healing process.
5. Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial to prevent the spread and recurrence of herpetic folliculitis. It is important to avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, and to wash hands regularly.
6. Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle modifications can help manage herpetic folliculitis effectively. These include getting enough rest, managing stress levels, and adopting a healthy diet to boost the immune system.
It is important to note that while these treatments can help manage herpetic folliculitis, there is currently no cure for the condition. The virus remains in the body even after symptoms have resolved, and outbreaks can recur in the future. Therefore, it is important to adopt preventive measures to minimize the risk of future outbreaks.
Herpetic Folliculitis: Prevention Tips
Preventing herpetic folliculitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of viral transmission and minimize the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Here are some tips to help prevent herpetic folliculitis:
#1. Practice good hygiene
Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after touching the affected area. Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels, lip balm, or razors, to prevent the spread of the virus.
#2. Avoid close contact with individuals experiencing an outbreak
Herpetic folliculitis is highly contagious during an outbreak. Avoid close contact, such as touching, kissing, or sharing utensils, with individuals experiencing active symptoms.
#3. Protect yourself during sexual activity
Use a barrier approach, such as condoms or dental dams, during sexual activity to reduce the risk of transmission.
#4. Manage stress
Stress can trigger outbreaks. Practice stress management techniques, like yoga, meditation, exercise, or therapy, to reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
#5. Protect your skin from excessive sun exposure
Use sunscreen or protective clothing to shield your skin from the sun’s harmful rays. Sunburns can trigger outbreaks in some individuals.
#6. Maintain a healthy immune system
A strong immune system can help prevent outbreaks. Get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and manage underlying health conditions to support your immune system.
By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of herpetic folliculitis and minimize the impact of outbreaks on your daily life. However, it is important to remember that even with preventive measures, the virus can still be transmitted, and outbreaks can occur.
Herpetic Folliculitis: Complications
In most cases, herpetic folliculitis is a self-limiting condition that resolves without complications. However, in some individuals, especially those with compromised immune systems, complications may arise. These complications can include:
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial or fungal infections may occur in the affected area, leading to additional symptoms, such as increased pain, swelling, or discharge.
- Spreading of the Virus: Herpetic folliculitis can spread to other parts of the body or to other individuals if proper preventive measures are not followed.
- Recurrent Outbreaks: The virus remains in the body even after symptoms have resolved. It can reactivate in the future, leading to recurrent outbreaks of herpetic folliculitis.
If you experience any complications or have concerns about your condition, it is important to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management.
The Takeaway
Herpetic folliculitis can be a bothersome and uncomfortable condition, but with the right knowledge and management strategies, you can take control of your skin health.
Remember, herpetic folliculitis is a viral infection that can be easily transmitted, so it is important to practice good hygiene and follow preventive measures. If you experience any complications or have concerns about your condition, it is essential to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management.
FAQs
Q: Can herpetic folliculitis be cured?
A: There is currently no cure for herpetic folliculitis. The virus remains in the body even after symptoms have resolved, and outbreaks can recur in the future.
Q: How long does an outbreak of herpetic folliculitis last?
A: The duration of an outbreak can vary from a few days to several weeks, depending on the individual’s immune response and the severity of the infection.
Q: Can herpetic folliculitis be sexually transmitted?
A: Yes, herpetic folliculitis can be sexually transmitted. It is important to practice safe sex and use barrier methods to reduce the risk of transmission.
Q: Can herpetic folliculitis be diagnosed through a blood test?
A: Yes, blood tests can be used to detect the presence of HSV antibodies in the blood, which can confirm the diagnosis of herpetic folliculitis.
Q: What is the difference between herpetic folliculitis and regular folliculitis?
A: Regular folliculitis is caused by bacteria, whereas herpetic folliculitis is caused by the herpes simplex virus. The symptoms and treatment options differ between the two.
Q: Is herpetic folliculitis contagious?
A: Yes, herpetic folliculitis is highly contagious. It can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or through sharing personal items.
Q: Can herpetic folliculitis recur?
A: Yes, herpetic folliculitis can recur, especially during periods of weakened immune function or stress. Proper management and preventive measures can help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Q: Can herpetic folliculitis lead to other complications?
A: In some cases, herpetic folliculitis can lead to complications such as secondary bacterial infections or the spread of the virus to other parts of the body. Prompt treatment and good hygiene practices can minimize the risk of complications.
Q: Can I prevent herpetic folliculitis?
A: While it may not be possible to completely prevent herpetic folliculitis, adopting good hygiene practices, avoiding direct contact with infected individuals, and maintaining a healthy immune system can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9675989/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16536821/
https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/22839
https://stdcenterny.com/articles/herpes-and-other-genital-sores.html
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/infectious-folliculitis?source=related_link
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12634996/