Vaginal Folliculitis: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
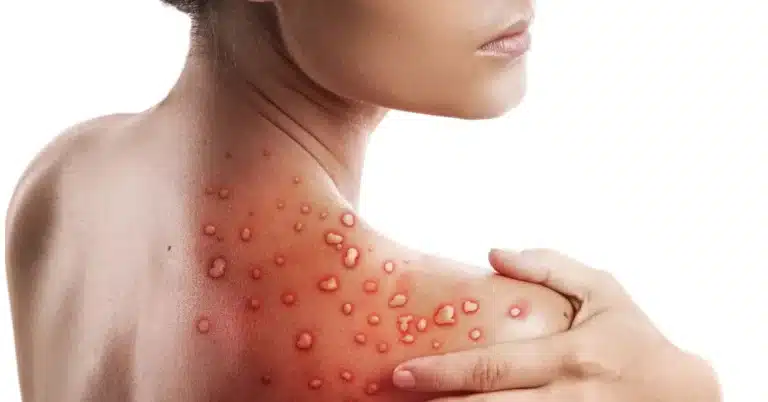
Vaginal folliculitis is a common condition that affects many women. It refers to the inflammation or infection of the hair follicles in the vaginal area. This condition can cause discomfort, itching, and pain, leading to significant distress for those affected.
This article aims to provide comprehensive information about vaginal folliculitis, including its symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures. Whether you are experiencing folliculitis on the vaginal lip, vulva, or hair near the vulva, this article will address your concerns and help you find relief.
Table Of Contents
- What is Vaginal Folliculitis?
- Symptoms of Vaginal Folliculitis
- Folliculitis Vulva: Understanding the Condition
- Treatment Options for Vaginal Folliculitis
- Preventing Folliculitis on Vulva/Vagina
- Dealing with Folliculitis on Hair Near Vulva
- Itchy Hair Follicles on Vulva: Causes and Remedies
- Folliculitis Vulva: Identifying and Treating Ingrown Hair Cysts
What Is Vaginal Folliculitis?
Vaginal folliculitis, or folliculitis on the vag lip or vulva, occurs when the hair follicles in the vaginal region become inflamed or infected. The primary cause of this condition is bacterial or fungal infection. It can also result from ingrown hairs or other irritants blocking hair follicles.
Common causes of vaginal folliculitis include poor hygiene, excessive sweating, friction from tight clothing, and shaving or waxing.
If you are experiencing vaginal folliculitis, it is significant to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Left untreated, folliculitis can worsen and cause discomfort or pain.
Symptoms Of Vaginal Folliculitis
When a woman experiences vaginal folliculitis, she may notice several symptoms that indicate the presence of this condition. Common symptoms include:
- Itching and irritation in the vaginal area
- Redness and swelling around the affected hair follicles
- Small, pus-filled bumps or pustules
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Discharge
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other vaginal infections. Therefore, consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis is crucial.
Folliculitis Vulva: Understanding The Condition
Folliculitis vulva refers to the inflammation of hair follicles on the vulva. It can cause discomfort, itching, and pain in the affected area. Folliculitis vulva can be caused by various factors, including bacteria, fungi, or viruses that enter the hair follicles. Certain conditions, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system, could also increase the risk of developing folliculitis vulva.
To effectively treat folliculitis vulva, a healthcare professional may recommend topical or oral medications to reduce inflammation and eliminate the underlying infection.
Treatment Options For Vaginal Folliculitis
Vaginal folliculitis can be effectively treated with proper care and medical interventions. The treatment options may vary depending upon the severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment methods for vaginal folliculitis:
1. Self-Care Measures
In mild cases, practicing good hygiene and keeping the affected area clean and dry may be sufficient to resolve the condition. Gently cleanse the genital area with mild, unscented soap and warm water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or excessive scrubbing, as this can further irritate the follicles.
Opt for loose-fitting, breathable underwear and clothing to reduce friction and allow the affected area to heal.
Temporarily refrain from removing hair in the affected area until the folliculitis has resolved to prevent further irritation and infection.
Avoid scratching or picking at the affected area to prevent further irritation or infection.
Applying warm compresses may help reduce inflammation.
2. Medications
Topical Creams or Ointments: Your healthcare provider may prescribe a topical antibiotic or antifungal cream to apply directly to the affected area to combat the infection and reduce inflammation.
Oral Antibiotics: In severe cases or when the infection spreads, oral antibiotics may be necessary to address the underlying bacterial infection.
3. Medical Procedures
Incision and Drainage: If a follicle becomes filled with pus or forms an abscess, a healthcare professional may need to make a small incision to drain the accumulated fluid and promote healing.
Laser Hair Removal: In cases where recurrent folliculitis is caused by ingrown hairs, hair removal through laser treatment can be an effective long-term solution to prevent further inflammation and infection.
Preventing Folliculitis On Vulva/Vagina
Preventing folliculitis on the vulva and vagina involves practicing good hygiene and adopting certain preventive measures. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of developing folliculitis:
- Maintain good personal hygiene by regularly washing the genital area with a mild, fragrance-free soap.
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting clothing that may cause friction and irritation.
- Use clean towels and avoid sharing personal items that come into contact with the genital area.
- If shaving or waxing the genital area, ensure proper hygiene and use clean and sharp razors or waxing tools.
- After shaving or waxing, apply a soothing, alcohol-free moisturizer to prevent dryness and irritation.
By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the chances of developing folliculitis on the vulva.
Dealing With Folliculitis On Hair Near Vulva
Folliculitis on hair near the vulva can be a persistent and bothersome condition. It can cause discomfort, itching, and unsightly bumps in the pubic region. To effectively deal with folliculitis on hair near the vulva, consider the following tips:
- Avoid excessive shaving or waxing, as it can irritate the hair follicles.
- If shaving, use a clean and sharp razor and follow proper shaving techniques.
- Gently exfoliate the pubic area to prevent the buildup of dead skin cells and bacteria.
- Apply warm compresses periodically to the affected area to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Use topical creams or ointments recommended by your healthcare professional to alleviate symptoms and eliminate the infection.
If the condition persists or worsens, it is essential to seek medical advice for further evaluation and treatment options.
Itchy Hair Follicles On Vulva: Causes and Remedies
Itchy hair follicles on the vulva can be a distressing symptom of vaginal folliculitis. Several factors can contribute to this sensation, including:
- Irritation from shaving or waxing.
- Allergic reactions to personal care products.
- Skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis.
- Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle.
To find relief from itchy hair follicles on the vulva, consider the following remedies:
- Avoid scratching the affected area to prevent further irritation and potential infection.
- Apply a soothing, fragrance-free moisturizer or hydrocortisone cream to alleviate itching.
- Use gentle, hypoallergenic personal care products and avoid harsh chemicals or fragrances.
- Wear loose-fitting cotton underwear to allow proper airflow and reduce friction.
Consult a healthcare expert for further evaluation and appropriate treatment options if the itching persists or worsens.
Folliculitis Vulva: Identifying And Treating Ingrown Hair Cysts
Ingrown hair cysts can be a complication of folliculitis vulva. These cysts occur when the hair follicles become blocked, leading to the accumulation of dead skin cells, bacteria, and trapped hair. They can cause pain, redness, and swelling in the affected area. To identify and treat ingrown hair cysts, consider the following steps:
- Gently cleanse the affected area with a mild, fragrance-free soap.
- Apply a warm compress to the cyst to promote drainage and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid squeezing or popping the cyst, as it can lead to further infection or scarring.
- If the cyst persists or becomes increasingly painful, seek guidance from a healthcare expert for proper evaluation and treatment options.
In some cases, a healthcare professional may need to drain the cyst or prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection.
Conclusion
Vaginal folliculitis can be a discomforting condition, but with proper understanding, timely treatment, and preventive measures, it can be effectively managed.
If you experience symptoms of vaginal folliculitis, seek guidance from a healthcare expert for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
By following the recommended guidelines and taking proactive steps, you can find relief from the symptoms and promote healing. Remember, maintaining good hygiene and practicing self-care are essential for the overall health and well-being of the vaginal area.
FAQs
Q: Can vaginal folliculitis be sexually transmitted?
No, vaginal folliculitis is not a sexually transmitted infection. It primarily results from bacterial or fungal overgrowth, irritants, or ingrown hairs. However, engaging in unprotected sexual activities can increase the risk of developing or aggravating the condition.
Q: Are there any home remedies for vaginal folliculitis?
While proper hygiene and self-care measures can help manage mild cases of vaginal folliculitis, it is advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare expert for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Home remedies alone may not be sufficient to resolve the condition completely.
Q: Can vaginal folliculitis recur?
Yes, vaginal folliculitis can recur, especially if the underlying causes are not addressed. To prevent recurrence, it is essential to practice good hygiene, avoid irritants, and adopt preventive measures discussed earlier.
Q: Can vaginal folliculitis be mistaken for other conditions?
Yes, the symptoms of vaginal folliculitis can sometimes resemble other conditions such as yeast infections or sexually transmitted infections. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis.
Q: Can stress contribute to vaginal folliculitis?
While stress itself may not directly cause vaginal folliculitis, it can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Managing stress through healthy coping mechanisms can help support overall well-being, including the prevention of vaginal folliculitis.
Q: Should I avoid sexual activity if I have vaginal folliculitis?
It is advisable to refrain from sexual activity until the symptoms of vaginal folliculitis have completely resolved. Engaging in sexual activity can cause further irritation and potentially spread the infection.
References
https://flo.health/menstrual-cycle/health/symptoms-and-diseases/vaginal-folliculitis
https://www.icliniq.com/articles/skin-care/vaginal-folliculitis
https://mycarmesi.com/blogs/f/vaginal-folliculitis
https://diag.vn/en/thongtinyte/causes-of-private-folliculitis/