Is Folliculitis Contagious? Understanding Acute Bacterial Skin Infections

“Folliculitis is generally not contagious, except in rare cases where the underlying infection can be transmitted through direct contact or shared personal items. Taking precautions and practicing good hygiene is important to prevent its spread.”
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it may seem like a minor annoyance, folliculitis can be contagious and spread rapidly if left untreated.
Many people are confused about the contagiousness of folliculitis, and this confusion can lead to the spread of the infection. In this article, we will clear up the confusion surrounding folliculitis contagiousness and provide you with tips on how to prevent its spread. We will discuss what folliculitis is, how it spreads, and the common symptoms to look out for.
We will also provide practical advice on how to prevent the spread of folliculitis, including hygiene tips, avoiding sharing personal items, and seeking timely medical treatment. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of folliculitis contagiousness and the measures you can adopt to ensure the safety of yourself and your loved ones.
So, let’s explore!
Table Of Contents
- What is Folliculitis?
- Types of Folliculitis
- What Causes Folliculitis?
- Symptoms of Folliculitis
- Folliculitis vs. Acne
- Treatment Options
- Complications and Recurrence
- Prevention and Home Care
- Folliculitis and Skin Care
- Natural Remedies For Folliculitis
- In A Nutshell
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is characterized by the inflammation of the hair follicles, which are small pockets in the skin from which hair grows. It occurs when bacteria, fungi, or viruses infect the hair follicles, leading to redness, swelling, and sometimes the formation of small pustules or blisters.
Folliculitis can affect any part of the body where hair is present, including the scalp, face, neck, arms, legs, and buttocks.
Types Of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can manifest in different forms depending on its underlying cause and the area of the body it affects. Each type of folliculitis has its own unique symptoms and contagion risks.
Two main types are superficial folliculitis and deep folliculitis. Some folliculitis types may only cause superficial symptoms and affect the upper part of the hair follicle. These infections typically appear as small, red, inflamed bumps that may contain pus.
Contrarily, deep folliculitis affects the deeper parts of the hair follicle and can be more severe. It often forms larger, painful, and pus-filled nodules or boils.
The most common types of folliculitis include:
1. Bacterial Folliculitis
It is caused by a bacterial infection, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, of the hair follicles. This type of folliculitis is highly contagious and can be easily spread through skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated items.
Symptoms of bacterial folliculitis include red, swollen, and painful bumps on the skin.
2. Fungal Folliculitis
Also known as tinea barbae is caused by a fungal infection of the hair follicles. This type of folliculitis is less contagious than bacterial folliculitis, and the contagiousness varies depending on the specific fungus involved.
Symptoms of fungal folliculitis include red, itchy, and scaly bumps on the skin.
3. Viral Folliculitis
Infections like herpes simplex virus or varicella-zoster virus can result in viral folliculitis. It is rare and is usually only seen in people with weakened immune systems. The contagiousness of viral folliculitis depends on the specific virus involved. Herpes simplex virus can be contagious through skin-to-skin contact during an active outbreak.
Symptoms of viral folliculitis include small, itchy bumps on the skin that may possibly be accompanied by fever and fatigue.
4. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Commonly known as razor bumps, this condition occurs when curved hair follicles grow back into the skin after shaving or waxing, causing inflammation and folliculitis.
5. Hot Tub Folliculitis
This type is caused by the bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which thrives in warm, contaminated water. It commonly occurs after using poorly maintained hot tubs or swimming pools. The symptoms may show up after one or two days post-bacterial exposure.
6. Eosinophilic Folliculitis
Eosinophilic folliculitis is a dermatological condition marked by the presence of itchy, red bumps or pustules that occur mainly on the upper body. Eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, are involved in the inflammation process.
7. Vaginal Folliculitis
Infection or inflammation of the hair follicles in the vaginal area. It can cause redness, itching, and discomfort. Good hygiene practices and avoiding irritants are important for prevention and treatment.
8. Folliculitis Decalvans
A chronic inflammatory scalp disorder characterized by the destruction of hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss. It presents as patches of hairless skin with redness, pustules, and scarring. Medical interventions may be necessary for management.
9. Pityrosporum Folliculitis
This form is caused by an overgrowth of yeast known as Malassezia. It often affects individuals with oily skin and causes itchy, acne-like lesions.
10. Drug-Induced Folliculitis
Folliculitis occurs as a side effect of certain medications. It manifests as small, red bumps or pustules on the skin. Identifying and discontinuing the offending drug is crucial for resolution.
11. Parasitic/Demodex Folliculitis
Caused by an infestation of the hair follicles by mites or lice. This type of folliculitis is highly contagious, and the transmission usually occurs through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated items.
Symptoms of parasitic folliculitis include intense itching and the presence of small, red bumps on the skin.
12. Gram-Negative Folliculitis
A bacterial infection that affects hair follicles is typically caused by certain types of bacteria known as Gram-negative bacteria. It commonly occurs as a complication of long-term antibiotic treatment for acne. It presents as pustules and nodules on the face, particularly in the nasal and perinasal areas.
13. Sycosis Barbae
Also known as barber’s itch, it is a bacterial infection that specifically targets the hair follicles in the beard and mustache area. It is usually triggered by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and commonly occurs due to shaving or other forms of hair removal.
Symptoms include redness, swelling, pustules, and crusting. Treatment may involve antibiotics and proper shaving techniques.
What Causes Folliculitis?
Understanding the causes of folliculitis is crucial in managing and preventing the condition. Here are some factors that contribute to its development:
- Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections
- Irritation from shaving or friction
- Trauma to the skin
- Compromised immune system
- Excessive sweating or humidity
- Occlusive clothing or tight fabrics
- Ingrown hairs
- Certain skin conditions, like acne or dermatitis
- Damaged hair follicles
- Excessive oil production
- Improper waxing
- Plucking
Symptoms of Folliculitis
The symptoms of folliculitis can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Small, red bumps or pimples around hair follicles
- Itching or tenderness in the affected areas
- Pus-filled blisters or sores
- Redness and inflammation around the hair follicles
- Burning sensation or pain in severe cases
- Potential hair loss in chronic or severe folliculitis
- Rash that may be painful
- Follicles with a central hair
- Pain or discomfort
- Development of crusts or scabs in chronic cases
It’s essential to note that symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of folliculitis.
Folliculitis vs. Acne
While folliculitis and acne may share some similarities, they are distinct conditions. Here’s how they differ:
Folliculitis primarily affects hair follicles, causing red, inflamed bumps, often filled with pus. Acne, on the other hand, involves the sebaceous glands and typically presents as blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts.
Folliculitis is often caused by bacteria, yeast, or physical irritation, whereas acne is primarily associated with hormonal imbalances and excess sebum production.
Treating folliculitis and acne may require different approaches, so it’s essential to differentiate between the two to determine the most effective course of action.
Treatment Options
The treatment of folliculitis depends on the severity and underlying cause. Treating folliculitis involves a combination of self-care measures and, in some cases, medical intervention. Here are some treatment options:
- Self-Care Measures: Mild cases of folliculitis often resolve on their own with proper self-care, such as applying warm compresses, avoiding shaving or irritating the affected area, and keeping the skin clean.
- Topical Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibacterial, antiviral, or antifungal creams, shampoos, lotions, or ointments to apply directly to the affected area.
- Oral Medications: In cases of widespread or recurrent folliculitis, oral antibiotics (such as dicloxacillin or cephalexin) or antifungal medications may be prescribed to combat the infection.
- Steroid Creams or Injections: Inflammation and itching can be reduced with the use of topical steroid creams or, in severe cases, corticosteroid injections.
- Procedural Interventions: In certain situations, procedures like incision and drainage may be recommended to manage chronic or deep-seated folliculitis.
- Laser Hair Removal: In cases of recurrent folliculitis due to ingrown hairs, laser hair removal can provide long-term relief by reducing hair growth.
It is advisable to follow your healthcare provider’s treatment recommendations and ensure diligent adherence to prescribed medications. Additionally, it’s important to avoid self-treatment with over-the-counter medications, as these can sometimes worsen the condition or cause unwanted side effects.
Complications and Recurrence
While most cases of folliculitis resolve with appropriate treatment, complications, and recurrences can occur. In rare cases, folliculitis can lead to complications, including:
- Cellulitis: A skin infection that can extend and spread to the surrounding tissues, causing redness, swelling, and warmth.
- Self-Inoculation: Scratching or touching the affected area and then touching other parts of the body can cause folliculitis to spread to new areas.
- Furuncles and Carbuncles: Severe cases of folliculitis can progress to furuncles (boils) or carbuncles (clusters of boils), requiring medical attention.
- Scarring or Hyperpigmentation: Prolonged or severe cases of folliculitis can result in permanent skin discoloration or scarring.
To cut down the risk of complications and recurrences, it’s important to follow the prescribed treatment plan and adopt preventive measures.
Prevention and Home Care
Preventing folliculitis involves practicing good hygiene and taking certain precautions. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly wash your skin with mild soap and water, especially after activities that may cause sweating or dirt accumulation.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, razors, clothing, or other personal items that may harbor bacteria or fungi.
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Dry your skin thoroughly after bathing or swimming, as moisture can promote bacterial or fungal growth.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing: Choose breathable fabrics and refrain from wearing tight clothing that may cause friction and irritation to the skin.
- Practice Safe Shaving/Waxing Techniques: Use clean razors or waxing tools and avoid shaving too closely or repeatedly in the same area to minimize skin irritation.
- Maintain Healthy Skin: Adopt a skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and exfoliation to keep the skin healthy.
Folliculitis and Skin Care
Proper skin care can play a significant role in managing and preventing folliculitis. Here are some tips to incorporate into your skincare routine:
- Choose Non-comedogenic Products: Opt for skin care products labeled as non-comedogenic, as they are less likely to clog hair follicles.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Harsh chemicals, such as alcohol-based toners or strong exfoliants, can irritate the skin and worsen folliculitis. Opt for gentle, pH-balanced products instead.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep the skin hydrated with a suitable moisturizer to prevent dryness, which can lead to irritation and inflammation.
- Don’t Overdo It: While exfoliating can help remove dead skin cells, overdoing it can strip the skin’s protective barrier and exacerbate folliculitis. Limit exfoliation to once or twice a week.
Natural Remedies For Folliculitis
While natural remedies may provide relief for mild cases of folliculitis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are some natural remedies that can complement medical interventions:
1. Essential Oils
Tea tree oil, geranium oil, neem oil, and grapefruit seed oil exhibit remarkable efficacy in the treatment of folliculitis.

- Incorporating tea tree oil into your shampoo, lotion, or body wash can prove beneficial. Massage gently onto affected areas and allow them to remain. Prior to usage, perform a patch test to ensure no adverse reactions occur. Tea tree oil is particularly advantageous for individuals experiencing recurrent folliculitis. To maximize its effects, tea tree oil can be combined with geranium oil and grapefruit seed oil.
- Neem oil, known for its potent antiseptic and antifungal properties, presents another powerful remedy. It also aids in preventing scar formation and effectively addresses skin and scalp infections. Blend neem oil with coconut oil or almond oil and massage gently onto affected areas. For optimal results, leave it on overnight. Alternatively, neem oil can be directly applied to the affected area. However, to ensure no adverse effects, conduct a small patch test beforehand.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel possesses potential healing properties that can accelerate skin recovery. Its cooling nature provides relief by soothing itching, redness, and swelling. Research indicates that aloe vera gel may also have antibacterial properties that can combat certain types of infection-causing bacteria.

When purchasing aloe vera gel, opt for a pure formulation without added perfumes or chemicals. After cleansing the area with soap and water, apply fresh aloe vera gel onto the affected areas to soothe inflammation and promote healing.
3. Warm Saltwater Soaks
Folliculitis often leads to inflamed swelling and irritation. To alleviate these symptoms, you can use a warm compress made by soaking a clean hand towel in salt water and then straining it.

This warm compress helps eliminate bacteria and fungus on the skin’s surface while promoting relaxation of the irritated skin, offering relief. Remember to repeat this process with fresh, clean towels and wash the used ones separately immediately afterward.
4. Turmeric Paste
Take several raw pieces of turmeric and soak them in water overnight. Afterward, blend all the pieces of raw turmeric until a fine paste is formed. Apply the blended turmeric paste onto the folliculitis blister and allow it to sit for a few hours before rinsing it off with regular water.

You can also mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste and apply it to the affected areas.
Turmeric is rich in medicinal properties, making it an excellent remedy for folliculitis. The application of turmeric paste helps alleviate the pain and swelling associated with the blister. Follow this home remedy for folliculitis twice a day on a regular basis.
5. Onion Juice
To prepare the remedy, start by crushing an onion until it forms a fine paste, and then strain the juice into a bowl. Next, take a few cotton buds and dip those buds into the onion juice and dab it over the affected areas. Try this remedy one or two times a day.

Onion has strong properties to treat folliculitis. This prevents swelling and reduces the effect of infection. This home remedy for folliculitis is one of the most effective and potent home remedies for folliculitis.
6. Yoghurt and Cumin Seed
Take a few spoons of cumin seeds and blend them until they form a fine powder. Mix a few tablespoons of cumin seed powder thoroughly with a few spoons of yogurt to create a smooth paste. Gently apply this paste to the infected area of your body affected by folliculitis and leave it on for a few hours before rinsing off with clean water.

Yogurt contains acidic properties that aid in reducing infection and killing bacteria. Cumin, known for its healing properties, further strengthens and enhances the effectiveness of this remedy. Follow this home remedy twice a day for optimal results.
7. Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a strong antiseptic that can help eliminate the bacteria or fungi causing your folliculitis. However, it’s essential to handle hydrogen peroxide with caution when using it at home, as it can be toxic if swallowed and may cause skin irritation if not applied correctly.
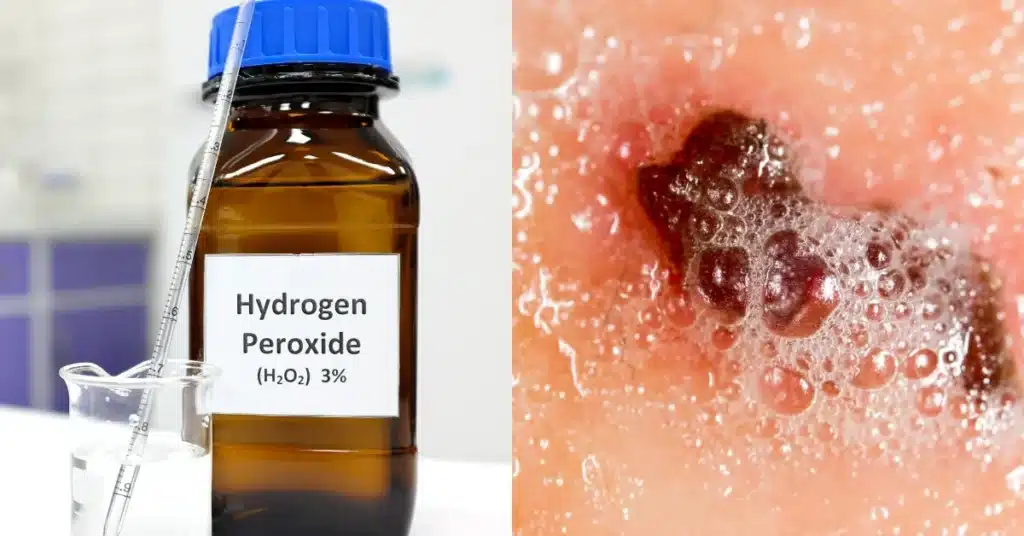
To use hydrogen peroxide, dilute the solution with some water. And then, dip a cotton ball into the mixture and gently apply it to the affected area.
8. Apple Cider Vinegar
According to a study by researchers from the University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, vinegar or acetic acid is shown to inhibit the growth of certain strains of bacteria. They studied the responses of many bacteria to vinegar and discovered that Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter, and Enterococcus faecalis were the most positively affected by vinegar at a concentration of 0.16 percent to 0.3 percent.

Apple cider vinegar usually has acidity levels between 2.5 and 3.0 percent. When you’re dealing with folliculitis, it’s important to dilute the vinegar before using it.
To make the vinegar solution, mix one tablespoon of vinegar with ½ cup of water. Use some cotton balls to soak in the mixture and apply them to the affected areas for 20 minutes twice a day. You should start seeing improvements within a few days, but for more severe cases, it might take a week or even longer.
For an even more comprehensive approach to folliculitis treatment, consider incorporating benzoyl peroxide and Hibiclens into your regimen. These powerful additions, when used alongside natural remedies, can help combat the infection, reduce inflammation, and promote a healthier skin environment.
Incorporate these remedies cautiously and discontinue use if any adverse reactions occur.
In A Nutshell
Understanding the various types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for folliculitis is essential for effective management. While folliculitis is generally not contagious, prompt treatment, good hygiene, and preventive measures are crucial to prevent complications and recurrence.
If you’re experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and guidance. By adopting appropriate care and seeking professional advice, you can effectively manage folliculitis and promote healthier skin.
FAQs
Q: Does folliculitis itch?
A: Yes, folliculitis can cause itching, although the intensity may vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause. Itching is commonly associated with folliculitis caused by yeast overgrowth, such as Pityrosporum folliculitis. Scratching the affected areas can further aggravate the condition and increase the risk of secondary infections.
Q: Can folliculitis spread?
A: Folliculitis is generally not contagious, except in rare cases where the underlying infection can be transmitted through direct contact or shared personal items.
Q: Is folliculitis curable?
A: Yes, most cases of folliculitis are curable with appropriate treatment and preventive measures.
Q: Can folliculitis cause hair loss?
A: Yes, folliculitis can cause hair loss if the condition is severe or chronic, as inflammation of the hair follicles can disrupt the hair growth cycle.
Q: What causes folliculitis on the scalp?
A: Folliculitis on the scalp can be caused by bacterial or fungal infections, viral infections, irritation or trauma to the scalp, and other factors like a weakened immune system or underlying skin conditions.
Q: What is the best shampoo for folliculitis?
A: Specific shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or salicylic acid may help manage folliculitis on the scalp.
Q: Is folliculitis contagious?
A: Folliculitis can be contagious if it is caused by bacteria or viruses. It is important to take precautions and practice good hygiene to prevent its spread.
Q: Can folliculitis spread after waxing?
A: Waxing can irritate the hair follicles, making them more susceptible to infection. It is crucial to adhere to proper aftercare instructions and maintain hygiene to prevent the spread of folliculitis.
References
https://www.healthline.com/health/is-folliculitis-contagious#summary
https://www.valleyskininstitute.com/folliculitis-home-treatment/